The nephroprotective potential of Sida cordata
10/30/2018 / By Ellaine Castillo
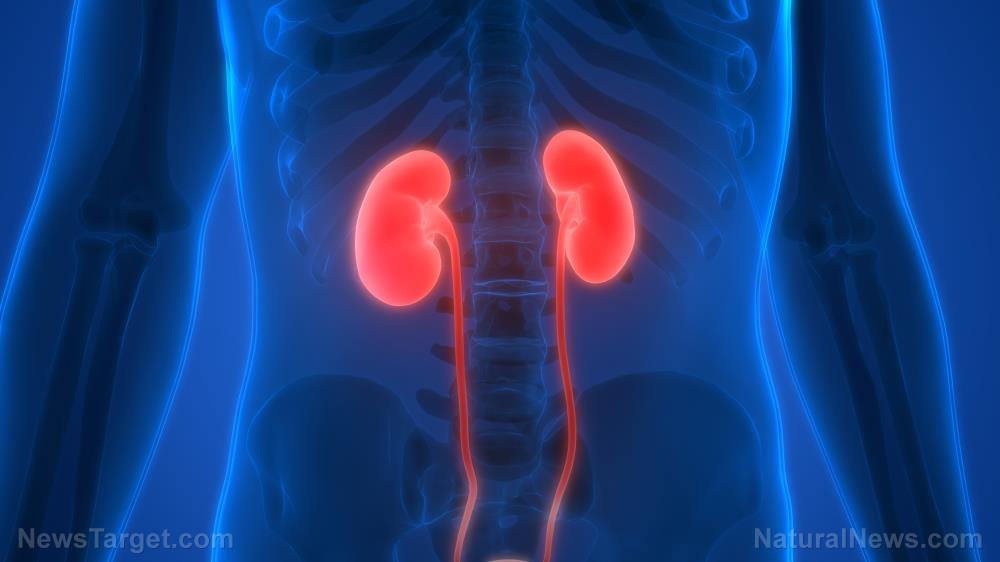
Kidneys are vulnerable to damage induced by free radicals, which can be caused by exposure to substances like carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Researchers from COMSATS Institute of Information Technology, Quaid-i-Azam University, and Ethiopian Public Health Institute have discovered that the plant Sida cordata can be used to treat CCl4-induced kidney damage. This finding, which was published in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, was based on in vivo experiments involving S. cordata ethyl acetate fraction.
- Substances like CCl4 induce kidney damage by triggering lipid peroxidation through its toxic metabolites, namely, trichloromethyl and trichloromethylperoxy radicals. Antioxidants work to prevent kidney damage by sequestering free radicals and preventing lipid peroxidation.
- Previous studies have shown the potent in vitro antioxidant activity of the ethyl acetate fraction of S. cordata.
- Antioxidant activity of S. cordata against CCl4-induced kidney damage was observed in male Sprague-Dawley rats.
- Presence of bioactive phytochemicals in S. cordata ethyl acetate fraction was determined using high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection (HPLC-DAD).
Results of the study show that the ethyl acetate fraction of S. cordata protects the kidney from CCl4-induced damage. Nephroprotective ability is possibly due to the presence of phytochemicals, such as gallic acid, catechin, and caffeic acid, which have potential antioxidant activity.
Read the full text of the study at this link.
Learn more about how Sida cordata can protect your kidney by visiting NaturalCures.news today.
Journal Reference:
Shah NA, Khan MR, Nigussie D. PHYTOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATION AND NEPHROPROTECTIVE POTENTIAL OF SIDA CORDATA IN RAT. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 4 August 2017;17(388). DOI:10.1186/s12906-017-1896-8
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, antioxidants, caffeic acid, Catechin, Gallic acid, herbal medicine, kidney damage, kidneys, lipid peroxidation, nephroprotective, nephrotoxicity, Sida cordata