How effective is panax notoginseng in the treatment of acute pancreatitis?
09/12/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
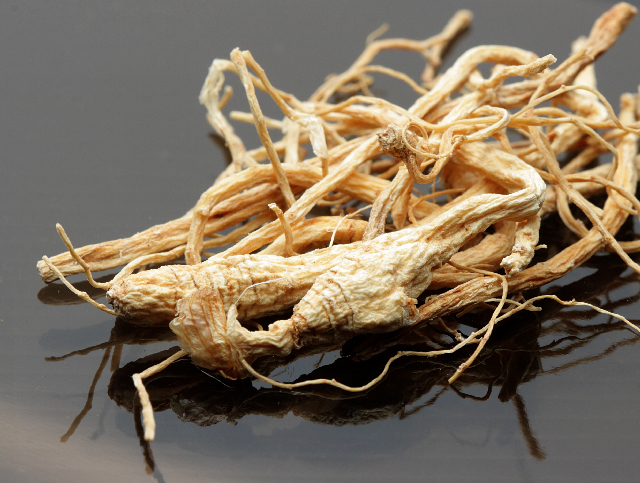

Chinese ginseng (Panax notoginseng), referred to as San Qi in China, has been found to potentially treat acute pancreatitis. In the study published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, the protective effects of Chinese ginseng saponins against acute pancreatitis were evaluated in a mouse model.
- Researchers from Kunming Medical University and its affiliated hospitals in Kunming, China initially administered Chinese ginseng saponins in the mice treatment group through intravenous injection.
- Two hours after, they administered taurocholate in mice to induce severe acute pancreatitis.
- After 24 hours, they measured the expression levels of miR-181b, microtubule-associated protein II light chain 3 (LC3-II), myosin-like B-cell lymphoma 2 (Blc-2) interacting protein (Beclin1), protein kinase B (Akt), and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways involved in the regulation of autophagy, which determines the development of pancreatitis.
- They also measured the expression levels of Caspase-3 and Blc-2, assessed apoptosis, and measured amylase and lipase in serum.
- Histological analysis was also conducted.
- Results revealed that Chinese ginseng increased the miR-181b expression level, which resulted in the significant reduction of pancreatic injury and autophagy and increases in apoptosis.
- The treatment also inhibited the formation of autophagosomes. The formation of autophagosomes is vital in pancreatitis development.
- In addition, it mitigated pancreatitis by reducing autophagy activation via increasing the mTOR/Akt pathway.
- It also reduced Bcl-2 expression, blocked autophagosome markers Beclin1 and LC3-11, and enhanced Caspase-3 expression.
- Chinese ginseng also significantly reduced serum lipase and amylase levels.
The findings of the study suggest that Chinese ginseng could potentially treat acute pancreatitis.
Read the full text of the study at this link.
To read more stories on Chinese medicines like Chinese ginseng, visit ChineseMedicine.news today.
Journal Reference:
Liu M, Wei R, Su M, Li H, Fang T, Zhang W. EFFECTS OF PANAX NOTOGINSENG SAPONINS ON SEVERE ACUTE PANCREATITIS THROUGH THE REGULATION OF MTOR/AKT AND CASPASE-3 SIGNALING PATHWAY BY UPREGULATING MIR-181B EXPRESSION IN RATS. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 5 February 2018; 18(51). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2118-8
Tagged Under: acute pancreatitis, alternative medicine, Chinese ginseng, Chinese medicine, ginseng, good herb, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural healing, natural medicine, natural remedies, Panax notoginseng, pancreatitis