Huang Qi, a foundational herb in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), found to inhibit breast cancer cell proliferation
09/08/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
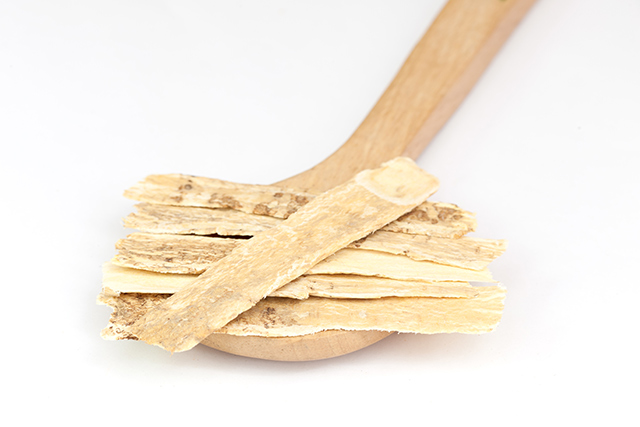

Huang qi (Astragalus membranaceus) is one of the fundamental herbs in traditional Chinese medicine, with earliest records of its use dating back over 2,000 years ago. Now, a study in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine has found that Huang qi is also able to prevent the spread of breast cancer cells in the body.
Breast cancer, in particular, is the most common cancer in women in the U.S., next to skin cancers. In fact, the current average risk of an American woman developing breast cancer in her lifetime is around 12 percent. This means that around one in eight women will develop the illness over the course of her lifetime. For 2018, approximately 266,120 new cases of invasive breast cancer will be diagnosed in women in the U.S., according to the estimates of the American Cancer Society.
In the study, researchers from the Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in China looked at how the Huang qi extract can affect breast cancer cells and the process behind this biological effect. They also looked at the primary isoflavones in the extract, as well as its anti-proliferative activity on three breast cancer lines: MCF-7 (ER+), SK-BR-3 (HER2+) and MDA-MB-231 (triple-negative). They did this by exposing these breast cancer cells to Huang qi extract for 48 hours.
In addition, they examined the effect of Huang qi extract on phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways, a primary intracellular signaling pathway that contributes to cell proliferation, growth, migration, metabolism, and apoptosis.
The power of the elements: Discover Colloidal Silver Mouthwash with quality, natural ingredients like Sangre de Drago sap, black walnut hulls, menthol crystals and more. Zero artificial sweeteners, colors or alcohol. Learn more at the Health Ranger Store and help support this news site.
The results of the study showed that the treatment of Huang qi extract exhibited anti-proliferative activity on breast cancer cells. Furthermore, the therapy promoted the death of breast cancer cells. These suggested that Huang qi’s ability to inhibit breast cancer cell growth was linked to its ability to inhibit PI3K/Akt/mTOR activity. Moreover, the researchers found that the Huang qi extract contains four types of isoflavones, such as campanulin, ononin, calycosin, and formononetin, which contributed to the inhibitory effect of Huang qi extract on breast cancer cells proliferation.
Huang qi and its medicinal uses
Huang qi, which means yellow leader, is a dried root of the astragalus herbal plant. Huang qi is well-known in China for its ability to boost the immune system, which also explains most of its benefits. (Related: How astragalus benefits people with cancer and low immunity.)
Some health benefits of Huang qi include:
- Treating the common cold and upper respiratory infections as it stimulates the immune system.
- Strengthening the body, especially during periods of immune deficiency.
- Helping the body avoid white blood cell deficiencies, such as leukopenia, which occur during chemotherapy.
- Protecting the body (including the liver) against bacteria, viruses, and inflammation.
- Supporting the digestive system, thanks to its diuretic properties.
- Treating skin disorders, such as burns and carbuncles, as well as hepatitis, chronic colitis, cardiovascular diseases, and viral conditions.
Huang qi can also be combined with other herbs, such as Dan Shen (Salvia) and Dang Gui (Angelica senesis root), to enhance their functions. This herb is sold in slices or small pieces. It can also be used alone, typically as a liquid extract or tea. This herb is also often used in cooking and can be added to soups, congees, stews, and other dishes to provide additional health benefits to the meal.
Read more news stories and studies on natural cancer treatments by going to CancerSolutions.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, astragalus, breast cancer, breast cancer cells, breast cancer treatment, cancer cures, cell proliferation, herbal medicine, herbal remedies, Herbs, huang qi, natural cures, natural healing, natural medicine, natural remedies, Oncology