Traditional ethnomedicine from Egypt proven to have strong antioxidant activity
07/19/2018 / By Edsel Cook
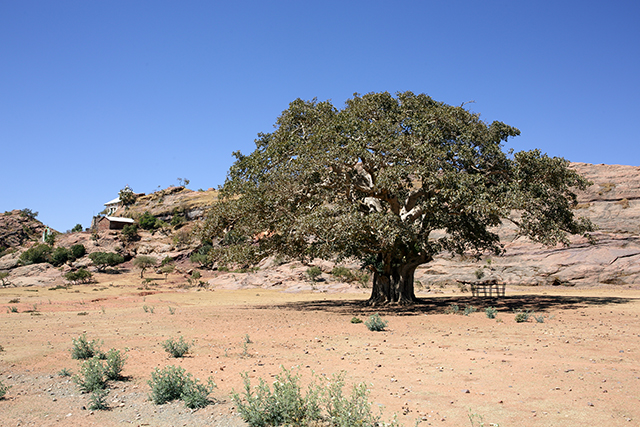

Traditional Egyptian medicine used the leaves of the warka fig (Ficus vasta) as a remedy for different kinds of diseases. A team of Italian researchers reported that a hydroalcoholic extract from the leaves of the indigenous tree contains phenolics with significant antimicrobial, antioxidant, and metal chelation activities.
The study was supported by the University of Messina. Its results were published in the science journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- Various tests were used to determine the phenolics in the warka extract. The antioxidant properties of these bioactive compounds were measured using in vitro systems.
- The extract was also tested on brine shrimp (Artemia salina) for potential toxicity to healthy cells. Its anti-microbial activity was tested on several Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains as well as the harmful yeast Candida albicans.
- The tests identified 12 different bioactive compounds in the warka extract. These substances were either phenolic acids or flavonoids.
- The warka extract was shown to scavenge large amounts of free radicals. It also showed strong reducing power and high chelating activity against toxic heavy metals.
- The extract completely protected against H202-induced damage from E. coli bacteria. It also stopped the reproduction of almost all the bacteria it was tested on. It did not harm the brine shrimp during the toxicity test.
The study concluded that warka fig leaves are a promising source of natural compounds that can neutralize harmful microbes, free radicals, and heavy metals without causing harm to healthy human cells.
Find the full text of the study at this link.
You can find articles about plant-based ethnomedicines at NaturalMedicine.news.
Journal Reference:
Taviano MF, Rashed K, Filocamo A, Cacciola F, Dugo P, Mondello L, Bisignano C, Acquaviva R, D’Arrigo M, Miceli N. PHENOLIC PROFILE AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF THE LEAVES OF FICUS VASTA FORSSK. (MORACEAE) GROWING IN EGYPT. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2018;18(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2210-0.
Tagged Under: Antibacterial activity, antibacterial properties, antioxidant activity, antioxidants, chelation, ethnomedicine, fig leaves, fig tree, herbal medicines, herbal remedies, Herbs, medicinal plants