Red sage found to prevent bone loss
12/26/2018 / By Zoey Sky

Experts warn that osteoporosis, a worldwide health problem, may affect at least one out of three women and one of out five men around the globe. Several studies have set out to determine a cure that can stop the progression of this condition, and according to researchers from the University of British Columbia, the answer could be found in a Chinese medicinal herb called red sage (Salvia Miltiorrhiza).
The study was published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.
Is red sage a natural cure for bone loss?
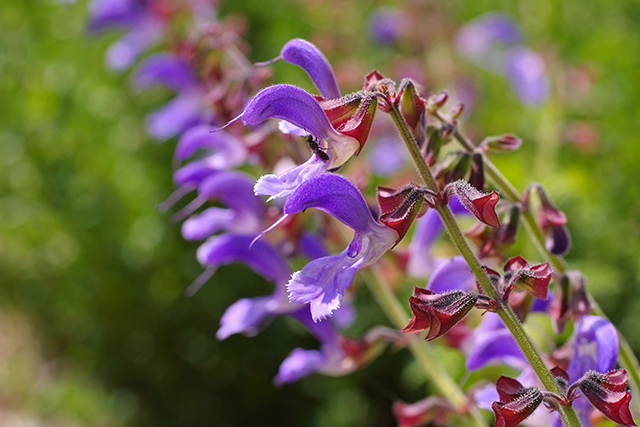
Red sage, called “danshen” in Chinese, is used in traditional medicine to treat bone ailments. The study findings suggest that the herb can potentially be used in a new osteoporosis therapy that prevents bone loss without causing negative side effects.
For the study, researchers who used a compound derived from red sage discovered a way to selectively block an enzyme called Cathepsin K (CatK). CatK has a crucial role in the breakdown of collagen in bones during osteoporosis.
Dieter Brömme, a professor in the faculty of dentistry and a Canada Research Chair in Proteases and Disease, explained that for the last few years, pharmaceutical companies worked tirelessly to develop osteoporosis drugs that could successfully block CatK. However, to date, all clinical trials have failed since the drugs caused harmful side effects such as cardiovascular issues, skin fibrosis, or stroke.
Brömme and the other researchers involved in the study found a natural way only to block CatK in bone tissue. The team is hopeful that doing so can help counter the side effects of the compound. (Related: Taking liquid calcium with red sage can build stronger bones.)
For the study, the researchers tested the compound derived from the red sage in human and mouse bone cells and a mouse model. The test results showed that the compound from the herb helped prevent bone loss. The mice treated with the red sage compound also had an increased bone mineral density of about 35 percent compared to the control group.
Brömme and his team referenced one of their earlier studies which that examined the effectiveness of red sage when used to halt the activity of CatK but only in limited ways, unlike other enzyme blockers or enzyme inhibitors.
Enzyme blockers function like keys in locks. The majority of drugs in development are active site-directed inhibitors that act like master keys and lock the entire enzyme. However, this blocks both its disease-relevant functions, like collagen degradation and its other normal functions. The researchers believe that red sage is a promising treatment for different kinds of bone and cartilage diseases, like arthritis and some types of bone cancers.
The medicinal uses of red sage
Red sage is used to treat various health problems, such as Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular conditions.
A study, which was published in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, reported that common traditional uses for red sage are for heart-related problems like angina, myocarditis, or heart attack.
Likewise, there are some studies which imply that red sage can help prevent some of the secondary concerns linked to diabetes like diabetic retinopathy or eye disease. A separate study published in Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine revealed that using danshen-dripping pills can improve visual function in individuals who had diabetic retinopathy.
Red sage is available as capsules, tea, or a tincture. Before you take red sage, consult a healthcare professional to determine the correct dosage for your condition.
Read more articles about the other health benefits of red sage at AlternativeMedicine.news.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
alternative medicine, bone diseases, bone health, bone loss, bone loss prevention, Cathepsin K, CatK, danshen, Enzymes, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural healing, natural medicine, natural remedies, osteoporosis, osteoporosis therapy, plant medicine, red sage, red salvia, Salvia miltiorrhiza
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
Herbs.News is a fact-based public education website published by Herbs News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Herbs News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.