Roselle displays potent antihypertensive effects
12/05/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
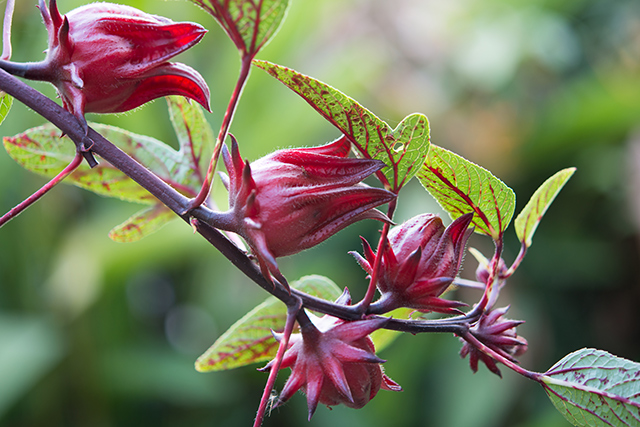

A team of researchers at Isfahan University of Medical Sciences in Isfahan, Iran have found that roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) contains powerful antihypertensive effects. They assessed the effects of roselle calyces on the serum levels of lipids and insulin, inflammation, and oxidative stress in patients with metabolic syndrome.
- For the study, which was published in the Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine, the research team recruited 40 adult participants with metabolic syndrome.
- Then, they randomly divided them into two groups: a treatment group and a placebo group.
- The treatment group received 500 milligrams (mg) of roselle calyx powder once a day for four weeks.
- On the other hand, the placebo group received a placebo once daily for four weeks.
- The researchers measured the participants’ systolic and diastolic blood pressures and body mass index (BMI) before and after the intervention.
- They also measured their fasting serum levels of glucose, insulin, lipoproteins, triglycerides, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and malondialdehyde (MDA) before and after the intervention.
- The results of the study showed that the treatment with roselle caused reductions in serum triglyceride levels and systolic blood pressure.
- Roselle treatment did not have a significant effect on all other variables.
- These results suggested that roselle has antihypertensive effects.
The findings of the study suggested that a daily intake of 500 mg of roselle calyx powder can lower systolic blood pressure and reduce serum triglyceride levels in people with metabolic syndrome.
To read more studies on roselle and other natural medicines, visit NaturalMedicine.news.
Journal Reference:
Asgary S, Soltani R, Zolghadr M, Keshvari M, Sarrafzadegan N. EVALUATION OF THE EFFECTS OF ROSELLE (HIBISCUS SABDARIFFA L.) ON OXIDATIVE STRESS AND SERUM LEVELS OF LIPIDS, INSULIN AND HS-CRP IN ADULT PATIENTS WITH METABOLIC SYNDROME: A DOUBLE-BLIND PLACEBO-CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL. Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine. 1 June 2016; 13(2): 175–180. DOI: 10.1515/jcim-2015-0030
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, antihypertensive, blood pressure, Florida cranberry, Heart, heart disease, heart health, herbal medicine, Herbs, Hibiscus sabdariffa, Jamaica sorrel, medicinal plants, metabolic syndrome, natural cures, natural healing, natural medicine, natural remedies, red sorrel, Roselle, triglycerides