The common purslane is a natural way to prevent diabetes
07/10/2018 / By Michelle Simmons

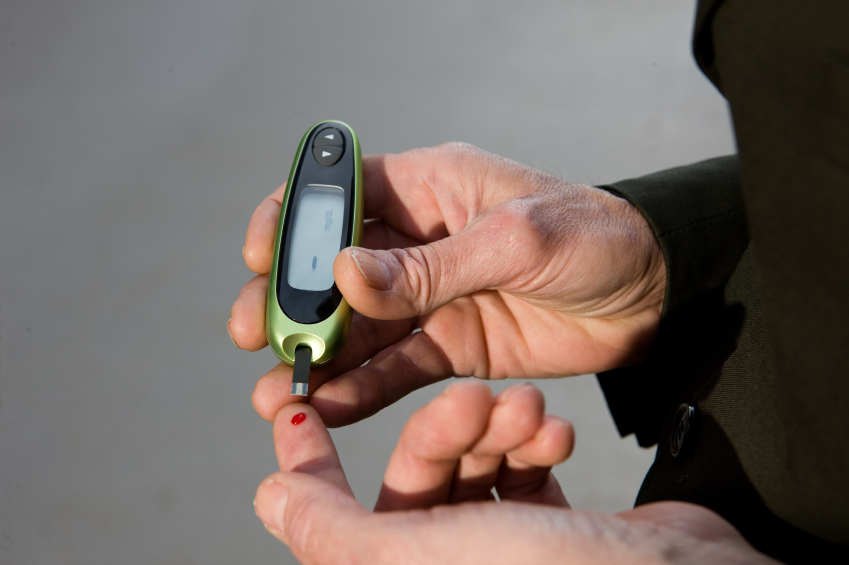
Prevent diabetes with the common purslane (Portulaca oleracea). In an animal study published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, the protective effects of the plant’s extract against diabetes were examined.
For the study, a team of researchers at Al-Azhar University and Misr International University in Egypt investigated four groups of mice: a control group; a group of healthy mice treated with common purslane extract at a daily dose of 250 milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg) for four weeks; an alloxan-induced diabetic control group; and an alloxan-induced diabetic group pretreated with common purslane extract at a daily dose of 250 mg/kg for four weeks.
The research team measured the body weight, food consumption, blood serum levels of glucose, C peptide, glycated hemoglobin (Hb A1C), insulin, tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and interleukin (IL)-6 of all mice in all groups.
Based on the results, the pretreatment of common purslane extract in the diabetic mice group resulted in great decreases in blood sugar levels. Histopathological tests also showed significant improvement in the damaging effect of the alloxan induction on pancreatic islet cells. As a result, the improved β-cell number and size, which are important targets in the management of diabetes, resulted in better insulin secretion and better glycemic control.
The research team also observed significant decreases in Hb A1C levels, which suggested that the total blood sugar levels were being more efficiently regulated because of the enhancements in insulin secretion. In addition, pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6, which are key factors in the progression of insulin resistance, were reduced in the mice pretreated with common purslane extract. These caused significant increases in C peptide and insulin, compared to the levels in counterpart diabetic mice group.
100% organic essential oil sets now available�for your home and personal care, including Rosemary, Oregano, Eucalyptus, Tea Tree, Clary Sage and more, all 100% organic and laboratory tested for safety. A multitude of uses, from stress reduction to topical first aid. See the complete listing here, and help support this news site.�
In conclusion, the findings of the study suggested that common purslane can help prevent diabetes by increasing β-cell mass, which in turn improved glucose metabolism.
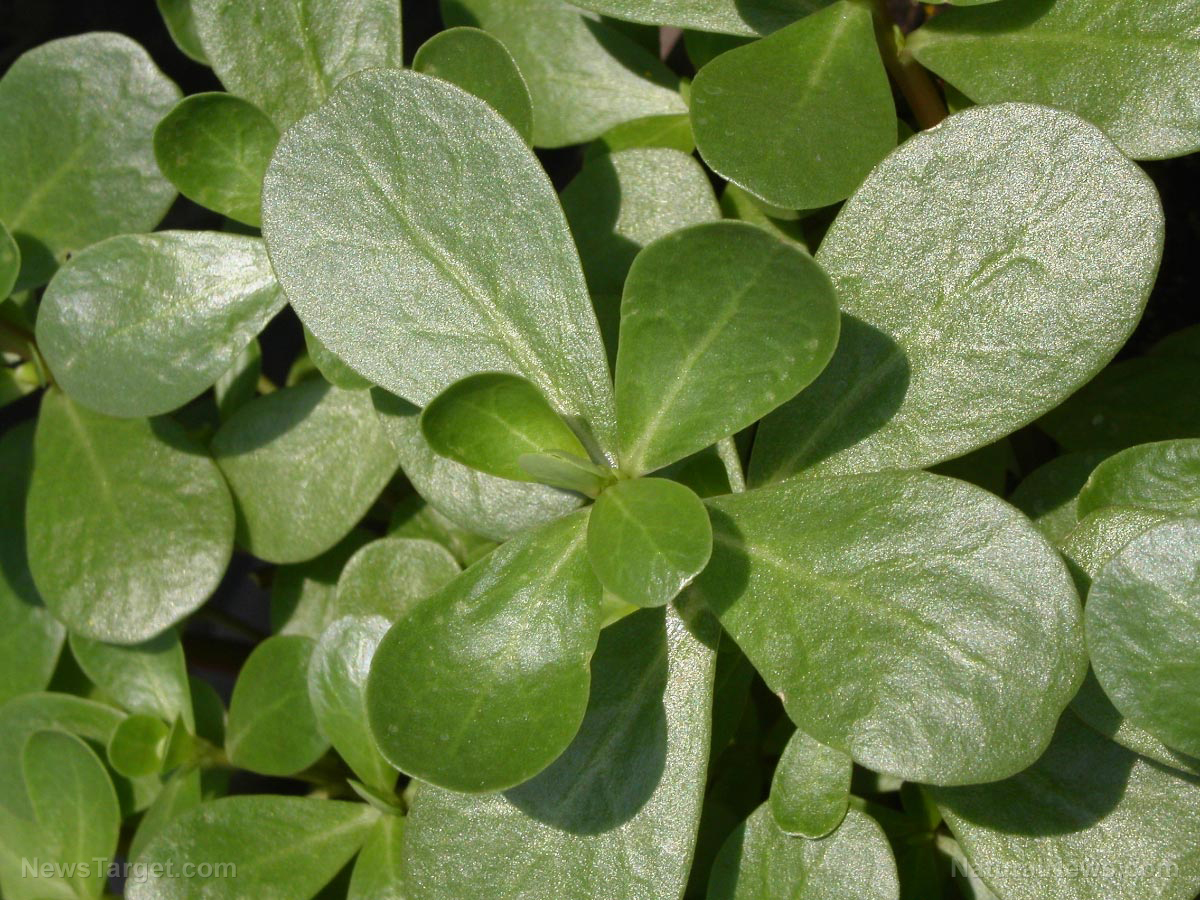
Common purslane and its nutritional profile
The common purslane plant is native to Persia, Africa, and India, but has now spread into Europe, Central America, and South America. This herb tends to grow in slightly damp or dry soil in vacant areas. It has tear-shaped leaves, yellow flowers, and slightly reddish-colored stem. This herb is also edible, with a slightly sour but sweet taste. Common purslane can be used in cooking, such as in salads, stir-fry dishes, soups, pickles, potato dishes, and casseroles. (Related: The incredible health benefits of purslane, a common edible garden weed.)
Although common purslane may just be a weed to some people, this plant is actually packed with nutritional value. In fact, it is considered as a “superweed.” Below is a list of nutrients that common purslane provides:
- Omega-3 fatty acids – The herb is one of the greatest sources of omega-3 fatty acids, containing more of the helpful substance than even some fish oils. One-hundred grams (g) of fresh purslane leaves contain approximately 350 milligrams (mg) of alpha-linolenic acid. Studies have shown that a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids may lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and help prevent the onset of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, and other developmental problems in children.
- Vitamin A – The herbal plant is one of the greatest sources of vitamin A among green leafy vegetables. Vitamin A is a powerful antioxidant that is beneficial for vision. Eating foods rich in vitamin A can help make the skin healthy and prevent lung and oral cavity cancers.
- Other vitamins and minerals – Common purslane is also a great source of B-vitamins, vitamin C, and dietary minerals, including iron, magnesium, calcium, potassium, and manganese.
- Antioxidants – The plant also contains two types of betalain alkaloid pigments – the reddish β -cyanins and the yellow β -xanthins. Research has shown that these antioxidants contain antimutagenic properties.
Read more news stories and studies on diabetes prevention by going to DiabetesScienceNews.com.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: diabetes, diabetes prevention, food as medicine, food cures, glucose levels, herbal medicine, herbal plants, Herbs, insulin, natural cures, natural medicine, Portulaca oleracea, prevention, purslane, superweed