A review of the anti-inflammatory effects of taraxasterol, a compound in dandelion, in animal models
04/17/2018 / By Edsel Cook
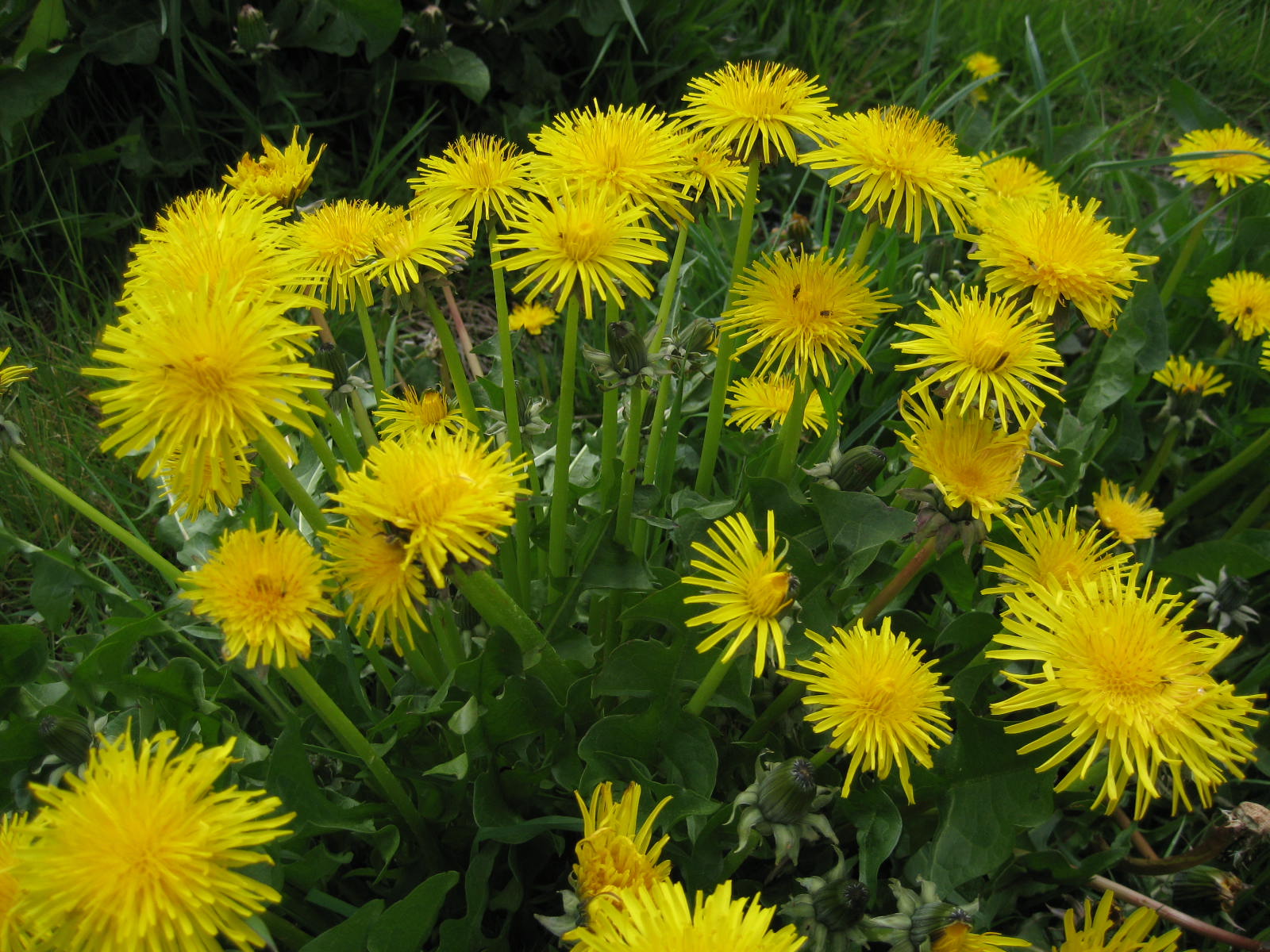

In a follow-up study, Chinese researchers from the Agricultural College of Yanbian University investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of taraxasterol, a natural compound found in the common dandelion (Taraxacum officinale). They determined that taraxasterol treatments successfully reduced swelling associated with ear and paw edema, vascular permeability, and granuloma in mouse and rat models. The research team published their findings in the African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines.
- Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) treats inflammation using herbal remedies derived from T. officinale. Taraxasterol was identified as one of the major active components in the herb.
- Recently, the Yanbian University team determined that taraxasterol possesses in vitro anti-inflammatory properties. They initiated an experiment to determine the compound’s effectiveness against acute and chronic inflammation in rodent models.
- Mice were used to model dimethylbenzene-induced ear edema and acetic acid-induced vascular permeability. Likewise, rats were used to generate models of carrageenan-induced paw edema and cotton pellet-induced granuloma.
- Each model was divided into five different groups. One was the control (placebo), three received different dosages of taraxasterol (2.5, five, and 10 milligrams/kilogram, respectively), and the positive treatment group received the common cough suppressant DXM (2.5 mg/kg).
- According to the study, taraxasterol attenuated inflammation in all animal models. As the dosage increased, so did its effectiveness. Taraxasterol compared favorably with DXM in reducing inflammation and associated symptoms.
The researchers believe their latest findings on taraxasterol’s efficacy in animal models supported TCM’s long-standing use of T. officinale-based treatments to alleviate inflammation in humans.
Find the full text of the study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Wang Y, Li GH, Liu XY, Xu L, Wang SS, Zhang XM. IN VIVO ANTI-INFLAMMATORY EFFECTS OF TARAXASTEROL AGAINST ANIMAL MODELS. African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative medicines. 2016;14(1):43–51. DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i1.6.
Tagged Under: anti-inflammatory, anti-inflammatory compounds, dandelions, herbal medicines, inflammation, taraxasterol, TCM, traditional Chinese medicine